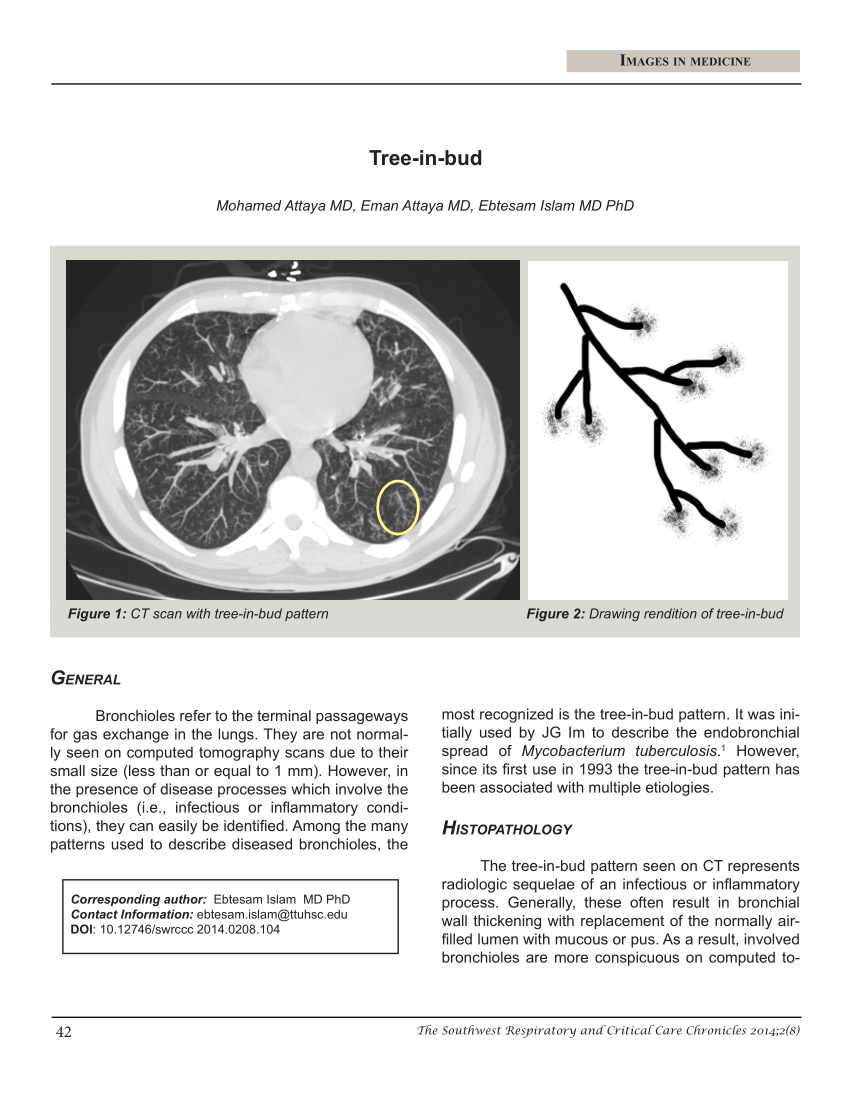
tree in bud opacities in lungs
87 rows Opportunistic lung infection in a 73-year-old female patient with selective IgG3 deficit. Note the peripheral tree-in-bud opacities.
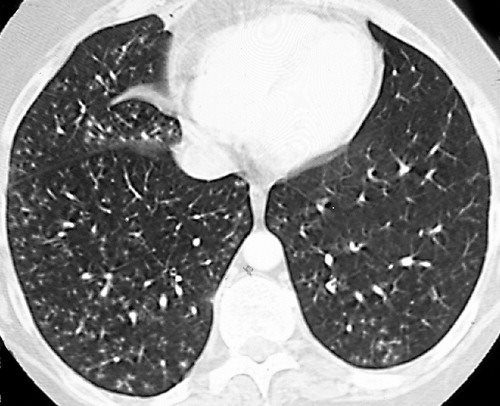
Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
CT-based analysis of.
. Although initially described in patients with endobronchial tuberculosis it is now recognized in a large number of conditions. What causes tree in bud opacities. The tree-in-bud pattern suggests active and contagious disease especially when associated with adjacent cavitary disease within the lungs.
HealthTap doctors are based in the US board certified and available by text or video. However in any individual case all causes of. Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery.
Bronchial disorders CT lung. There are widespread TIB opacities throughout both lungs with predominance in the anterior nondependent portions of the lungs a finding that would normally suggest a diagnosis other than aspiration. Distal pulmonary vasculature More specifically the pattern can be manifest because of the following disease processes often in combination.
Coronal reconstructed computed tomography image shows the lingular cavity with irregular nodules and right mid-lung nodular opacities in a 43-year-old man who. Distal airways more common 2. Although initially described in 1993 as a thin-section chest CT finding in active tuberculosis TIB opacities are by.
The tree-in-bud pattern or sign should be used in case of visible tree and bud. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. The most common CT findings are centrilobular nodules and branching linear and nodular opacities.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a subset of centrilobular nodules. Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. There are widespread TIB opacities throughout both lungs with predominance in the anterior nondependent portions of the lungs a finding that would normally suggest a diagnosis. Radiologic-Pathologic Overview RadioGraphics Vol.
Rossi SE et al Tree-in-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs. The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. 1 refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Fig.
Video chat with a US. In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. We here describe an unusual cause of TIB during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Although initially described in patients with endobronchial tuberculosis it is now recognized in a large number o. Ad Get the Latest On The First Signs of Lung Cancer In This Article. Board-certified doctor 247 in less than one minute for common issues such as.
TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping. TIB opacities represent a normally invisible branches of the bronchiole tree 1 mm in diameter that are severely impacted with mucous pus or fluid with resultant dilatation and budding of the terminal bronchioles 2 mm in diameter 1 photo. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
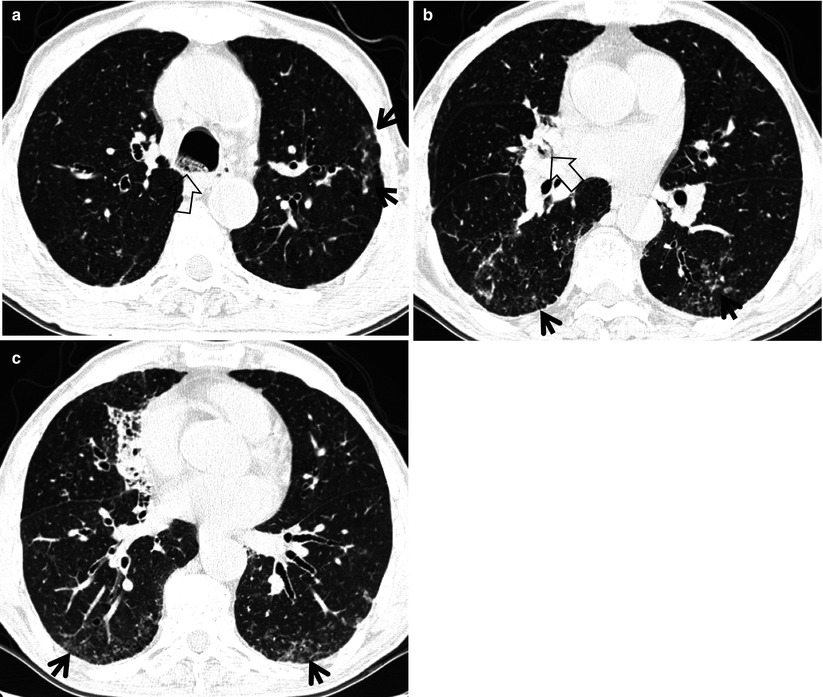
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. The differential for this finding includes malignant and inflammatory etiologies either infectious or sterile. The examination shows a nearly uniform distribution of TIB opacities arrows across the lungs bilaterally.
Get prescriptions or refills through a video chat if the doctor feels. We suggest that clusters of micronodules on CT in adult active pulmonary tuberculosis represent aggregated tree-in-bud lesions. PDF We report a clinical case of mentally challenged young gentleman who was repeatedly hospitalized for respiratory symptoms.
Alternating areas of normal lung with regions of small airways disease TIB opacities bronchiectasis random small airways pattern was specific 092 for Mycobacterium. 11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan.
High-resolution CT scans show enlarged and beaded subsegmental arteries in the lower lobes. Simply put the tree-in-bud pattern can be seen with two main sites of disease 3. 11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background.
It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk. 3 found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in. The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs.
CT finding of centrilobular nodules with TIB opacities was first described in pulmonary tuberculosis and is considered highly predictive of. Tree-in-bud sign lung Tree-in-bud sign or pattern describes the CT appearance of multiple areas of centrilobular nodules with a linear branching pattern. Bronchiolesfilled with pus or inflammator.
The term centrilobular branching opacity is desirable in case the bud is absent. Tree-in-bud sign or pattern describes the CT appearance of multiple areas of centrilobular nodules with a linear branching pattern. A young male patient who had a history of fever cough and respiratory distress presented in the emergency department.
Originally reported in cases of endobronchial spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis this. 3 2005 Tumor emboli from Ewing sarcoma in a 16-year-old boy. Causes for TIB.
High-resolution CT scan. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung.
Colds and coughs stomach symptoms bladder infections rashes and more. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. TIB opacities typically show branching configurations from secondary pulmonary lobules with sparing of subpleural lungs on CT thorax.
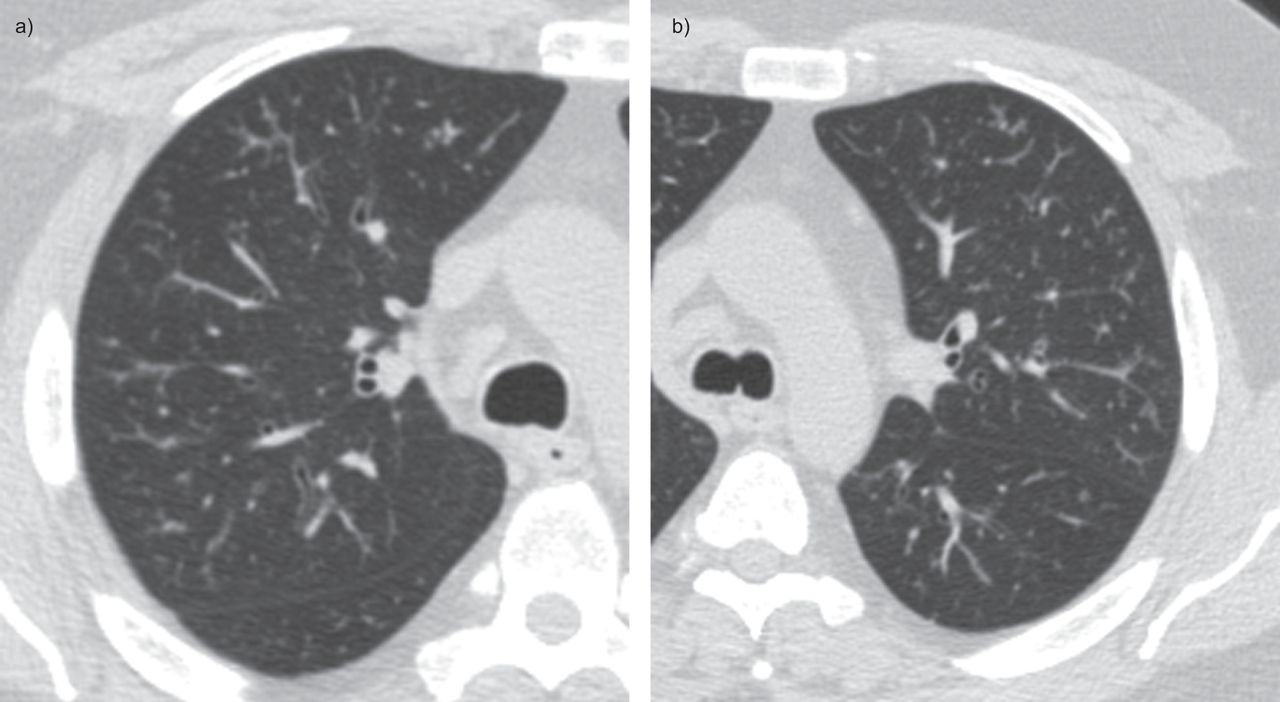
Hypereosinophilic Obliterative Bronchiolitis A Distinct Unrecognised Syndrome European Respiratory Society
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

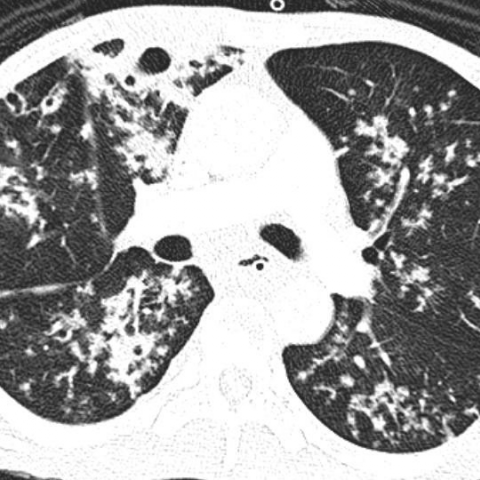
Ct Scan Of Chest Revealing Scattered Tree In Bud Opacities In Both Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Sign Radiology Key
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
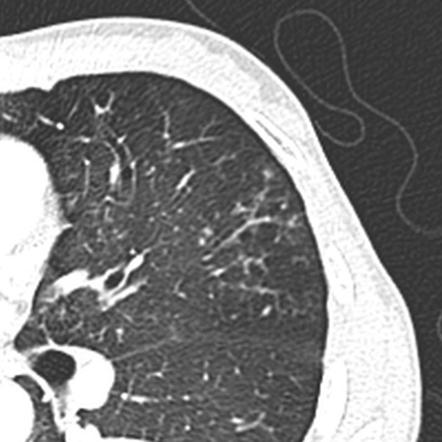
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Sign And Bronchiectasis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Signs And Patterns Of Lung Disease Chest Radiology The Essentials 2nd Edition